A-Z Of Quantitative Pcr Pdf Download
Background Currently real time PCR is the most precise method by which to measure gene expression. The method generates a large amount of raw numerical data and processing may notably influence final results. The data processing is based either on standard curves or on PCR efficiency assessment. At the moment, the PCR efficiency approach is preferred in relative PCR whilst the standard curve is often used for absolute PCR.
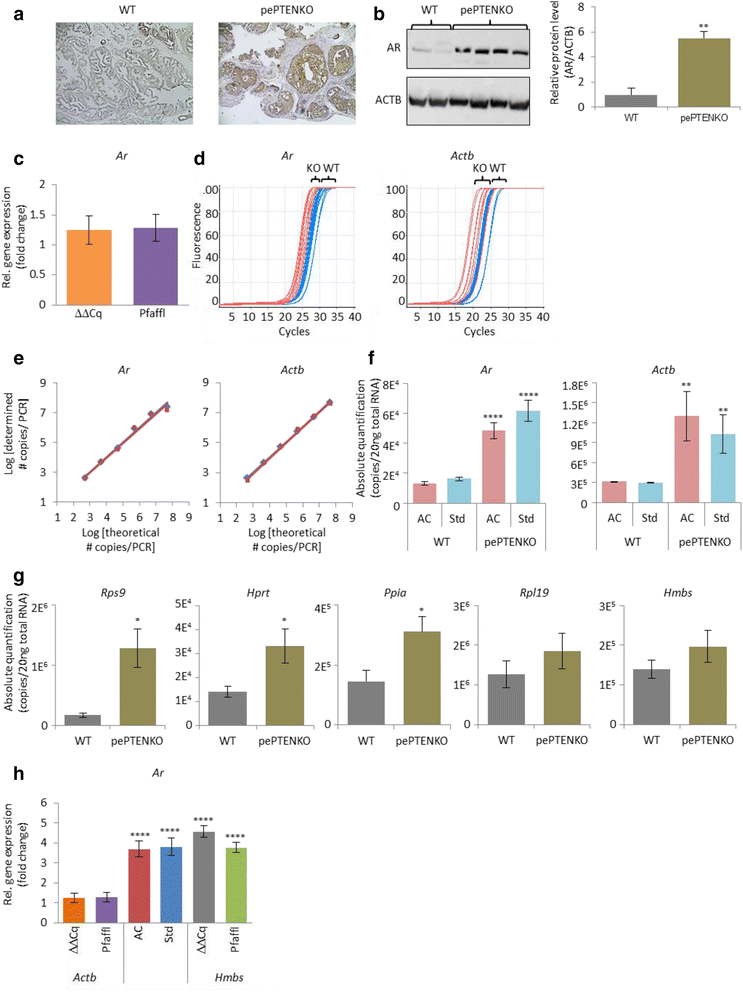
(Cq) values obtained by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis in an RNA interference (RNAi) experiment. In this study, the human aldolase A (ALDOA).
Under “Target Account”, enter the username. It will open the following view. Under “Target IP Server”, enter the IP of the server holding the SQL. Smtp cracking tutorials.
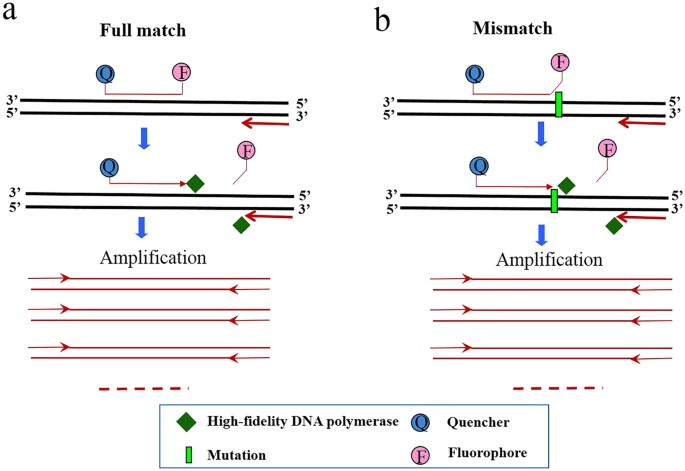
However, there are no barriers to employ standard curves for relative PCR. This article provides an implementation of the standard curve method and discusses its advantages and limitations in relative real time PCR. Results We designed a procedure for data processing in relative real time PCR. The procedure completely avoids PCR efficiency assessment, minimizes operator involvement and provides a statistical assessment of intra-assay variation. The procedure includes the following steps. (I) Noise is filtered from raw fluorescence readings by smoothing, baseline subtraction and amplitude normalization.
(II) The optimal threshold is selected automatically from regression parameters of the standard curve. (III) Crossing points (CPs) are derived directly from coordinates of points where the threshold line crosses fluorescence plots obtained after the noise filtering.
(IV) The means and their variances are calculated for CPs in PCR replicas. (V) The final results are derived from the CPs' means. The CPs' variances are traced to results by the law of error propagation. A detailed description and analysis of this data processing is provided. The limitations associated with the use of parametric statistical methods and amplitude normalization are specifically analyzed and found fit to the routine laboratory practice. Different options are discussed for aggregation of data obtained from multiple reference genes.
Background Data processing can seriously affect interpretation of real time PCR results. In the absence of commonly accepted reference procedures the choice of data processing is currently at the researcher's discretion. Many different options for data processing are available in software supplied with different cyclers and in different publications [-]. However, the basic choice in relative real time PCR calculations is between standard curve and PCR-efficiency based methods. Compared to the growing number of studies addressing PCR efficiency calculations [,,-] there is a shortage of publications discussing practical details of the standard curve method []. As a result, the PCR efficiency approach appears as the method of choice in data processing for relative PCR [].
However, when reliability of results prevails over costs and labor load, the standard curve approach may have advantages. The standard curve method simplifies calculations and avoids practical and theoretical problems currently associated with PCR efficiency assessment. Widely used in many laboratory techniques this approach is simple and reliable. Moreover, at the price of a standard curve on each PCR plate it also provides the routine validation for methodology. To benefit from the advantages of the standard curve approach and to evaluate its practical limitations we designed a data processing procedure implementing this approach and validated it for relative real time PCR. Transformation of the Normal distribution through PCR data processing was analyzed by a computer simulation. It showed that the shape of resulting distributions significantly depends on the initial data dispersion.