Adam Equity Theory Of Motivation Pdf
John Stacey Adams' equity theory helps explain why pay and conditions alone do not determine motivation. It also explains why giving one person a promotion. Captain america avenger hindi dubbed download 2016. Appear to be more sensitive to equity. Equity theory, as developed by Adams (1965), considers motivation and job satisfaction as the result of a comparison of a.
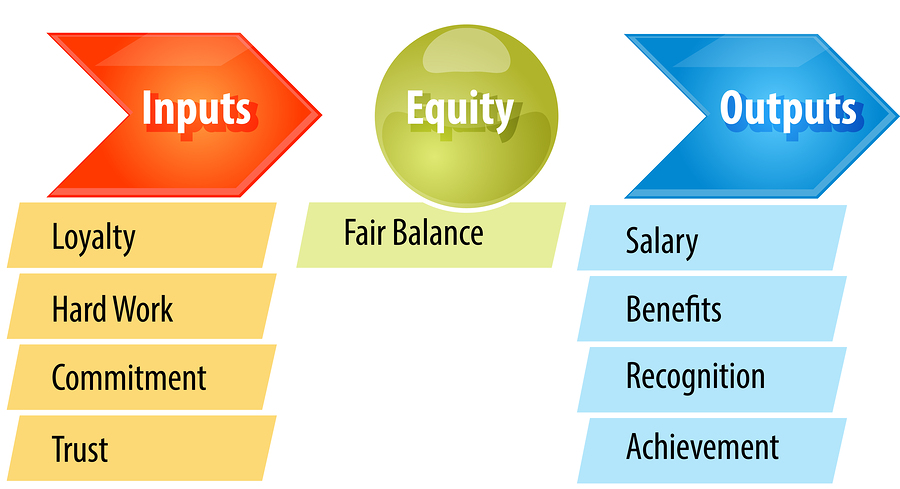
Equity theory, most popularly known as equity theory of, was first developed by John Stacey Adams, a workplace and behavioral psychologist, in 1963. John Stacey Adams proposed that an employee’s is affected by whether the employee believes that their employment benefits/rewards are at least equal to the amount of the effort that they put into their work. Definition of equity An individual will consider that he is treated fairly if he perceives the ratio of his inputs to his outcomes to be equivalent to those around him. Thus, all else being equal, it would be acceptable for a more senior colleague to receive higher, since the value of his experience (and input) is higher. The way people base their experience with for their job is to make comparisons with themselves to people they work with. If an employee notices that another person is getting more recognition and rewards for their contributions, even when both have done the same amount and quality of work, it would persuade the employee to be dissatisfied.
This dissatisfaction would result in the employee feeling under-appreciated and perhaps worthless. This is in direct contrast with the idea of equity theory, the idea is to have the rewards (outcomes) be directly related with the quality and quantity of the employees contributions (inputs). If both employees were perhaps rewarded the same, it would help the workforce realize that the organization is fair, observant, and appreciative. This can be illustrated by the following equation: Adam’s categorised employment benefits and rewards as outputs and an employee’s work effort as inputs.
This article may require to meet Wikipedia's. No has been specified. Please help if you can. ( October 2011) () () Equity theory focuses on determining whether the distribution of resources is fair to both relational partners. Equity is measured by comparing the ratio of contributions (or costs) and benefits (or rewards) for each person. Considered one of the justice theories, equity theory was first developed in the 1960s by J. Stacy Adams, a and, who asserted that employees seek to maintain equity between the inputs that they bring to a job and the outcomes that they receive from it against the perceived inputs and outcomes of others (Adams, 1963).
The belief is that people value fair treatment which causes them to be motivated to keep the maintained within the relationships of their co-workers and the organization. The structure of equity in the workplace is based on the ratio of inputs to outcomes. Inputs are the contributions made by the employee for the organization. Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Background [ ] Equity theory focuses on determining whether the distribution of resources is fair to both relational partners. It proposes that individuals who perceive themselves as either under-rewarded or over-rewarded will experience distress, and that this distress leads to efforts to restore equity within the. It focuses on determining whether the distribution of resources is fair to both relational partners.
Equity is measured by comparing the of contributions and benefits of each person within the relationship. Partners do not have to receive equal benefits (such as receiving the same amount of love, care, and financial security) or make equal contributions (such as investing the same amount of effort, time, and financial resources), as long as the ratio between these benefits and contributions is similar. Much like other prevalent theories of motivation, such as, equity theory acknowledges that subtle and variable individual factors affect each person’s assessment and perception of their relationship with their relational partners (Guerrero et al., 2005).
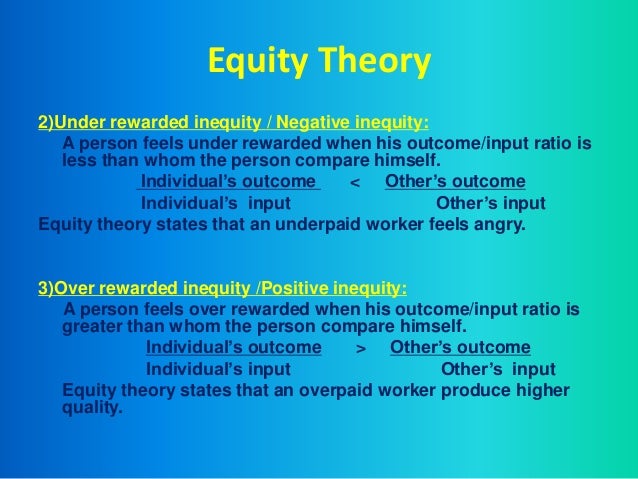
According to Adams (1965), anger is induced by underpayment inequity and guilt is induced with overpayment equity (Spector 2008). Payment whether hourly wage or salary, is the main concern and therefore the cause of equity or inequity in most cases. In any position, an employee wants to feel that their contributions and work performance are being rewarded with their pay. If an employee feels underpaid then it will result in the employee feeling hostile towards the organization and perhaps their co-workers, which may result in the employee not performing well at work anymore. It is the subtle variables that also play an important role in the feeling of equity.
Just the idea of recognition for the job performance and the mere act of thanking the employee will cause a feeling of satisfaction and therefore help the employee feel worthwhile and have better outcomes. Definition of equity [ ] Individuals compare their job inputs and outcomes with those of others and then respond to eliminate any perceived inequities. Referent Comparisons: Inputs and outcomes [ ] Inputs [ ] Inputs are defined as each participant’s contributions to the relational exchange and are viewed as entitling him/her to rewards or costs. The inputs that a participant contributes to a relationship can be either assets – entitling him/her to rewards – or liabilities - entitling him/her to costs. The entitlement to rewards or costs ascribed to each input vary depending on the relational setting. In industrial settings, assets such as capital and manual labor are seen as 'relevant inputs' – inputs that legitimately entitle the contributor to rewards.